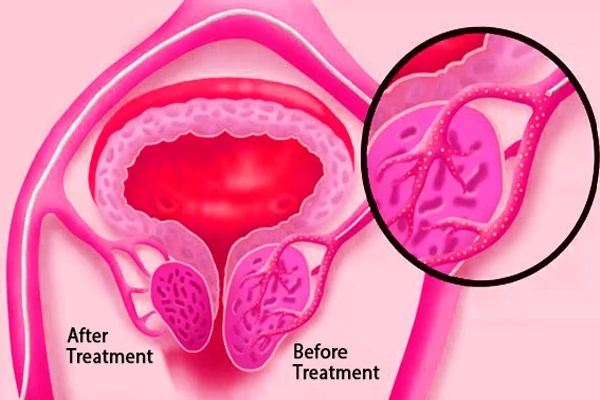
What happens during a PAE procedure?
- Once patient is taken in the procedure room and prepared for the procedure, local ananesthesia is applied to numb your wrist or groin area.
- After that, a needle is inserted to assist in the placement of a catheter, led by an X-ray technique called fluoroscopy to access the blood vessels supplying the prostate.
- After that, an arteriogram is done by introducing a contrast dye to visualize the blood supply to the prostate. With the visualisation of artery clear, a synthetic embolic agent, resembling grains of sand, will be injected through the catheter.
- These will block the blood flow to the prostate vessels, so it is starved of its blood supply. The procedure is continued for few more minutes till complete blood flow obstruction is achieved.
- The catheter will then be repositioned on the opposite side of the prostate, and the process is repeated. During the procedure, patient will lie on comfortably on his back and will be awake throughout the procedure.
- Typically the procedure completed in under an hour, than the patient is shifted to private room for recovery.
How long does the PAE procedure take?
Time taken to perform the procedure varies and depends on the severity of the condition. Mostly the duration of a prostate artery embolization or PAE is around one to one and half hours. Patients are able to go home the same day. Recovery is fast and only takes a few days before patients can go about their normal routine and return to work.
How long does a patient need to stay in the hospital?
Patients will need to stay in the hospital for one day for the prostate artery embolization procedure.
Do I need to stay fasting for the PAE procedure?
Yes. Similar to any other medical procedure involving intervention and anesthesia, patients do need to stay fasting for 6 hours before the procedure.
Does PAE hurt?
No. Prostatic Artery Embolisation / PAE does not cause pain to the patients, and hence patients are not administered general anesthetic. Local anaesthesia is applied at the location from where the catheter is inserted which is away from the actual prostate location. Post the procedure is completed, the catheter is withdrawn. Patient may feel a warm sensation when the beads are injected but no pain. In certain patients, if patients are too anxious sedative may be administered by the clinicians.
Will PAE cause incontinence?
Incontinence is a common possible side effect of TURP. TURP is a surgery which requires inserting a resectoscope into the tip of the penis. PAE is not established to cause incontinence.
Is PAE performed through the penis?
No. Nothing goes in or via your penis. PAE is performed inside arteries. For which catheter is inserted either via wrists or thigh/groin.
What is the PAE success rate?
Prostate artery embolization has a very high success rate. About 95% of the patients enjoy symptomatic relief. After the procedure, patients can once again enjoy a normal, relaxed life. Approximately six months after PAE, the prostate normally reduces in size by about 40%. This reduction allows the urethra to decongest or open up and urine flows more normally. Prostate size shrinkage via PAE does not harm sexual function.
PAE remains the first choice of treatment for its benefits. Also if for any clinical reason, the procedure doesn´t provide relief, the patient can still opt for surgical options. However vice versa is not possible.
Will PAE in any way affect my ability to have children?
No. PAE does not affect fertility. Rather it has been reported that some men experience improvement in their sexual performance.
Does insurance cover prostate artery embolization?
Yes. Most insurance carriers cover PAE. Please check with your insurance provider to see if your specific plan covers the procedure. Our team at the endovascular clinic will be happy to help you with your Mediclaim.
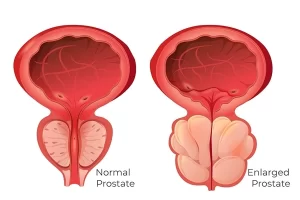
What is prostate artery embolization (PAE)?
Prostate artery embolization (PAE) is a non-surgical minimally invasive procedure for treating prostate enlargement. Tiny/ Very small microspheres are injected into the blood vessels (arteries) which supply to the prostate gland. These microspheres block off the blood flow causing the swelling in the prostate glad thus reducing the size of prostate.