Understanding How Prostate Enlargement Happens

What Is The Prostate Gland
The prostate is a gland. Glands are a type of tissue that produces & releases substances that perform certain functions. There are various glands in the human body with different functions to perform. It is part of the male reproductive system that produces a part of the fluid that makes up semen. The prostate does not release sperm itself but a portion of semen which is important for carrying sperm. Sperms are produced in the testicles and not the prostate.
Anatomy
The prostate is a rubber gland approximately the size of a ping-pong ball. It is located below the bladder between the base of the penis and the rectum. The urethra which is a tube that carries urine from the bladder passes through the middle of the prostate along the length of the penis. The urethra is the same tube in which the prostate releases the part of semen that helps carry sperm produced in the testes.
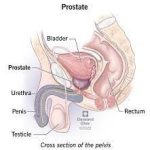
Prostate Enlargement
When young, the prostate is small, but as one gets older it grows. As the prostate grows, it begins to press or squeeze the urethra which can make it harder for men to urinate. If you have an enlarged prostate, you’ll notice that you’re having trouble urinating. Instead of having a strong even flow, the urine only dribbles out. Because you’re not emptying your bladder fully each time, you keep feeling the urge to use the bathroom, even in the middle of the night.
Enlargement of the Prostate also known as Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH) is one condition that is believed that every man will develop if he lives long enough. Statistical analysis of isolated geographies has revealed that 90% of males over the age of 80 years do display the existence of Prostate enlargement or BPH. It is a condition that is mostly observed to develop past the age of 40 years.
What Causes Prostate Enlargement Or BPH
There is no specific reason identified for growth in prostate size. There are certain factors though which are believed to have an impact on the growth of the prostate gland.
- Aging
- Changes in cells of testicles
- Hormonal changes – levels of testosterone hormone
Risks With Prostate Enlargement
BPH is not cancerous, nor does it contribute to prostate cancer. Prostate enlargement is not a fatal condition but compromises the quality of life for the patient significantly. It leads to complications such as urinary tract infections, bladder stones, kidney damage, and sexual dysfunction.
There are various treatments available for BPH. All types – surgical, and non-surgical options, medications are available to treat the condition and you may read here to learn about them.